| Home | All Classes | Main Classes | Annotated | Grouped Classes | Functions |
The TQDockWindow class provides a widget which can be docked inside a TQDockArea or floated as a top level window on the desktop. More...
#include <qdockwindow.h>
Inherits TQFrame.
Inherited by TQToolBar.
This class handles moving, resizing, docking and undocking dock windows. TQToolBar is a subclass of TQDockWindow so the functionality provided for dock windows is available with the same API for toolbars.
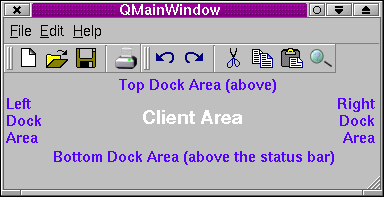
Two TQDockWindows (TQToolBars) in a TQDockArea
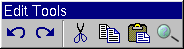
A Floating TQDockWindow
If the user drags the dock window into the dock area the dock window will be docked. If the user drags the dock area outside any dock areas the dock window will be undocked (floated) and will become a top level window. Double clicking a floating dock window's titlebar will dock the dock window to the last dock area it was docked in. Double clicking a docked dock window's handle will undock (float) the dock window. If the user clicks the close button (which does not appear on dock windows by default - see closeMode) the dock window will disappear. You can control whether or not a dock window has a close button with setCloseMode().
TQMainWindow provides four dock areas (top, left, right and bottom) which can be used by dock windows. For many applications using the dock areas provided by TQMainWindow is sufficient. (See the TQDockArea documentation if you want to create your own dock areas.) In TQMainWindow a right-click popup menu (the dock window menu) is available which lists dock windows and can be used to show or hide them. (The popup menu only lists dock windows that have a caption.)
When you construct a dock window you must pass it a TQDockArea or a TQMainWindow as its parent if you want it docked. Pass 0 for the parent if you want it floated.
TQToolBar *fileTools = new TQToolBar( this, "File Actions" );
moveDockWindow( fileTools, Left );
In the example above we create a new TQToolBar in the constructor of a TQMainWindow subclass (so that the this pointer points to the TQMainWindow). By default the toolbar will be added to the Top dock area, but we've moved it to the Left dock area.
A dock window is often used to contain a single widget. In these cases the widget can be set by calling setWidget(). If you're constructing a dock window that contains multiple widgets, e.g. a toolbar, arrange the widgets within a box layout inside the dock window. To do this use the boxLayout() function to get a pointer to the dock window's box layout, then add widgets to the layout using the box layout's TQBoxLayout::addWidget() function. The dock window will dynamically set the orientation of the layout to be vertical or horizontal as necessary, although you can control this yourself with setOrientation().
Although a common use of dock windows is for toolbars, they can be used with any widgets. (See the TQt Designer and TQt Linguist applications, for example.) When using larger widgets it may make sense for the dock window to be resizable by calling setResizeEnabled(). Resizable dock windows are given splitter-like handles to allow the user to resize them within their dock area. When resizable dock windows are undocked they become top level windows and can be resized like any other top level windows, e.g. by dragging a corner or edge.
Dock windows can be docked and undocked using dock() and undock(). A dock window's orientation can be set with setOrientation(). You can also use TQDockArea::moveDockWindow(). If you're using a TQMainWindow, TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow() and TQMainWindow::removeDockWindow() are available.
A dock window can have some preferred settings, for example, you can set a preferred offset from the left edge (or top edge for vertical dock areas) of the dock area using setOffset(). If you'd prefer a dock window to start on a new line when it is docked use setNewLine(). The setFixedExtentWidth() and setFixedExtentHeight() functions can be used to define the dock window's preferred size, and the setHorizontallyStretchable() and setVerticallyStretchable() functions set whether the dock window can be stretched or not. Dock windows can be moved by default, but this can be changed with setMovingEnabled(). When a dock window is moved it is shown as a rectangular outline, but it can be shown normally using setOpaqueMoving().
When a dock window's visibility changes, i.e. it is shown or hidden, the visibilityChanged() signal is emitted. When a dock window is docked, undocked or moved inside the dock area the placeChanged() signal is emitted.
See also Main Window and Related Classes.
This enum type specifies when (if ever) a dock window has a close button.
This enum specifies the possible locations for a TQDockWindow:
If p is InDock, the dock window is docked into a dock area and parent must be a TQDockArea or a TQMainWindow. If the parent is a TQMainWindow the dock window will be docked in the main window's Top dock area.
If p is OutsideDock, the dock window is created as a floating window.
We recommend creating the dock area InDock with a TQMainWindow as parent then calling TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow() to move the dock window where you want it.
Returns the dock area in which this dock window is docked, or 0 if the dock window is floating.
If the dock window only needs to contain a single widget use setWidget() instead.
See also setWidget() and setOrientation().
Returns the close mode of a dock window. See the "closeMode" property for details.
If the dock window has no last dock area (e.g. it was created as a floating window and has never been docked), or if the last dock area it was docked in does not exist (e.g. the dock area has been deleted), nothing happens.
The dock window will dock with the dock area regardless of the return value of TQDockArea::isDockWindowAccepted().
See also undock(), TQDockArea::moveDockWindow(), TQDockArea::removeDockWindow(), TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow(), TQMainWindow::removeDockWindow(), and TQDockArea::isDockWindowAccepted().
See also setFixedExtentWidth() and setFixedExtentHeight().
See also closeMode.
Returns TRUE if the dock window is horizontally stretchable; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "horizontallyStretchable" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the user can move the dock window within the dock area, move the dock window to another dock area, or float the dock window; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "movingEnabled" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the dock window is resizeable; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "resizeEnabled" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the dock window is stretchable in the current orientation(); otherwise returns FALSE. See the "stretchable" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the dock window is vertically stretchable; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "verticallyStretchable" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the dock window prefers to start a new line in the dock area; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "newLine" property for details.
Returns the dock window's preferred offset from the dock area's left edge (top edge for vertical dock areas). See the "offset" property for details.
Returns TRUE if the dock window will be shown normally whilst it is being moved; otherwise returns FALSE. See the "opaqueMoving" property for details.
See also orientationChanged().
This signal is emitted when the orientation of the dock window is changed. The new orientation is o.
This function returns where the dock window is placed. This is either InDock or OutsideDock.
See also TQDockArea::moveDockWindow(), TQDockArea::removeDockWindow(), TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow(), and TQMainWindow::removeDockWindow().
This signal is emitted when the dock window is docked (p is InDock), undocked (p is OutsideDock) or moved inside the the dock area.
See also TQDockArea::moveDockWindow(), TQDockArea::removeDockWindow(), TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow(), and TQMainWindow::removeDockWindow().
Sets the close mode of a dock window to m. See the "closeMode" property for details.
See also setFixedExtentWidth().
See also setFixedExtentHeight().
Sets whether the dock window is horizontally stretchable to b. See the "horizontallyStretchable" property for details.
Sets whether the user can move the dock window within the dock area, move the dock window to another dock area, or float the dock window to b. See the "movingEnabled" property for details.
Sets whether the dock window prefers to start a new line in the dock area to b. See the "newLine" property for details.
Sets the dock window's preferred offset from the dock area's left edge (top edge for vertical dock areas) to o. See the "offset" property for details.
Sets whether the dock window will be shown normally whilst it is being moved to b. See the "opaqueMoving" property for details.
Warning: All undocked TQToolBars will always have a horizontal orientation.
Sets whether the dock window is resizeable to b. See the "resizeEnabled" property for details.
Sets whether the dock window is vertically stretchable to b. See the "verticallyStretchable" property for details.
See also boxLayout().
Undocks the TQDockWindow from its current dock area if it is docked; otherwise does nothing.
See also dock(), TQDockArea::moveDockWindow(), TQDockArea::removeDockWindow(), TQMainWindow::moveDockWindow(), and TQMainWindow::removeDockWindow().
This signal is emitted when the visibility of the dock window relatively to its dock area is changed. If visible is TRUE, the TQDockWindow is now visible to the dock area, otherwise it has been hidden.
A dock window can be hidden if it has a close button which the user has clicked. In the case of a TQMainWindow a dock window can have its visibility changed (hidden or shown) by clicking its name in the dock window menu that lists the TQMainWindow's dock windows.
See also setWidget().
This property holds the close mode of a dock window.
Defines when (if ever) the dock window has a close button. The choices are Never, Docked (i.e. only when docked), Undocked (only when undocked, i.e. floated) or Always.
The default is Never.
Set this property's value with setCloseMode() and get this property's value with closeMode().
This property holds whether the dock window is horizontally stretchable.
A dock window is horizontally stretchable if you call setHorizontallyStretchable(TRUE) or setResizeEnabled(TRUE).
See also resizeEnabled.
Bugs and limitations:
Set this property's value with setHorizontallyStretchable() and get this property's value with isHorizontallyStretchable().
This property holds whether the user can move the dock window within the dock area, move the dock window to another dock area, or float the dock window.
This property is TRUE by default.
Set this property's value with setMovingEnabled() and get this property's value with isMovingEnabled().
This property holds whether the dock window prefers to start a new line in the dock area.
The default is FALSE, i.e. the dock window doesn't retquire a new line in the dock area.
Set this property's value with setNewLine() and get this property's value with newLine().
This property holds the dock window's preferred offset from the dock area's left edge (top edge for vertical dock areas).
The default is 0.
Set this property's value with setOffset() and get this property's value with offset().
This property holds whether the dock window will be shown normally whilst it is being moved.
If this property is FALSE, (the default), the dock window will be represented by an outline rectangle whilst it is being moved.
Warning: Currently opaque moving has some problems and we do not recommend using it at this time. We expect to fix these problems in a future release.
Set this property's value with setOpaqueMoving() and get this property's value with opaqueMoving().
This property holds whether the dock window is resizeable.
A resizeable dock window can be resized using splitter-like handles inside a dock area and like every other top level window when floating.
A dock window is both horizontally and vertically stretchable if you call setResizeEnabled(TRUE).
This property is FALSE by default.
See also verticallyStretchable and horizontallyStretchable.
Set this property's value with setResizeEnabled() and get this property's value with isResizeEnabled().
This property holds whether the dock window is stretchable in the current orientation().
This property can be set using setHorizontallyStretchable() and setVerticallyStretchable(), or with setResizeEnabled().
See also resizeEnabled.
Bugs and limitations:
Get this property's value with isStretchable().
This property holds whether the dock window is vertically stretchable.
A dock window is vertically stretchable if you call setVerticallyStretchable(TRUE) or setResizeEnabled(TRUE).
See also resizeEnabled.
Bugs and limitations:
Set this property's value with setVerticallyStretchable() and get this property's value with isVerticallyStretchable().
This file is part of the TQt toolkit. Copyright © 1995-2007 Trolltech. All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2007 Trolltech | Trademarks | TQt 3.3.8
|